Introduction
EIGRP Protocol is a product of the Cisco Systems company and can be said to have been born in the early 1990s. The main focus for using this protocol is to share routing information in the fastest way possible while at the same time enjoying the benefits offered by the protocol.
In this blog, we will discuss EIGRP, exploring its features, benefits, and how it works. We will also discuss its advantages over other routing protocols and provide examples of how it’s used in real-world networking scenarios. Whether you’re a network administrator, a student of computer science, or simply interested in learning about networking protocols, this blog will provide you with a good understanding of this protocol and its importance in modern networking.
Before getting into more details, let us first understand what it is.
What is EIGRP?
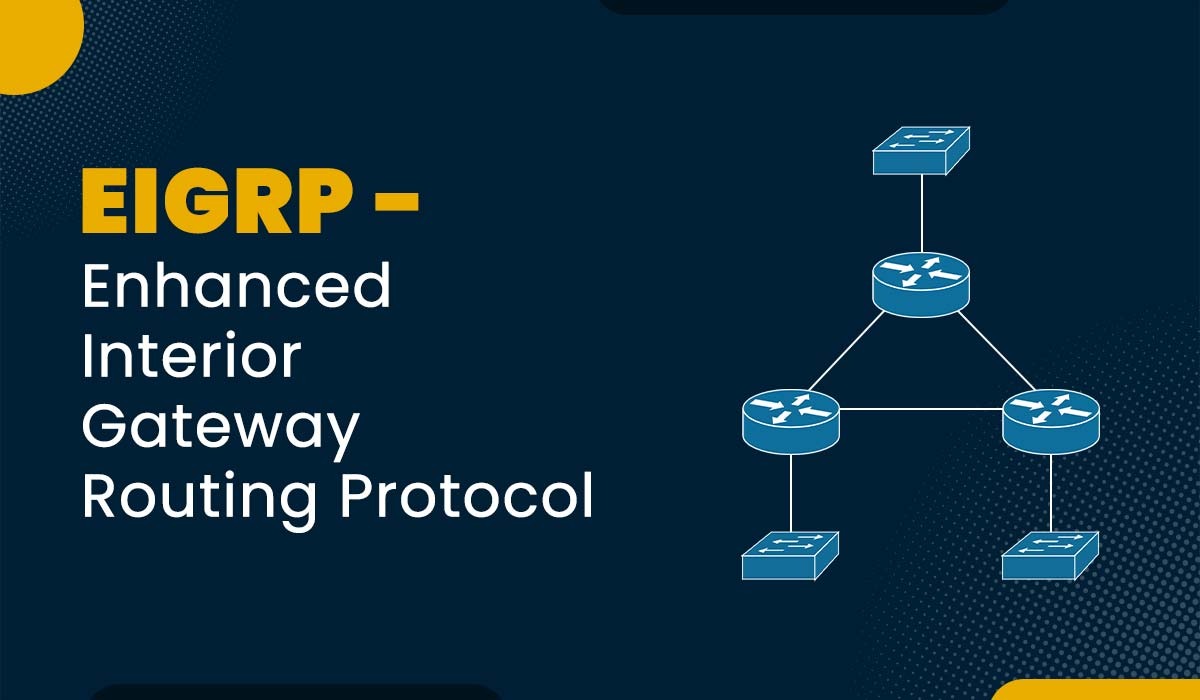
EIGRP stands for Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol. It is the modern distance-vector routing protocol designed and developed by Cisco Systems to distribute or transmit information in a network. It enhances the capabilities of Interior Gateway Routing Protocol more commonly known as IGRP. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol combines the advantages of link-state and distance-vector protocols, enabling efficient routing within an autonomous system. It supports rapid convergence, scalability, and multiple network layer protocols, making it suitable for diverse networks.
Initially, EIGRP protocol became an open standard in 2013 which means it became compatible with network systems of other vendors. This was achieved when it was updated to an open standard, which made significant advancements by making its usage more widespread in different networks.
Now that you have a basic understanding of the EIGRP protocol. Let us now discuss its features.
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol Features
Below, we have discussed some of the features of this protocol.
Rapid Convergence
It uses DUAL as its routing algorithm to help rebuild the routing table when there are any changes in the network. It quickly adapts to network failures, maintaining uptime by automatically reconfiguring routes and ensuring efficient data flow without manual intervention.
Scalability
It effectively finds the best routes in large and complicated networks without being limited by the network’s size or structure. It enhances enterprise network performance by providing scalable routing solutions that maintain high service quality, ensuring efficient data transmission without degradation, regardless of network size or complexity. Thus, presenting future-ready network possibilities.
Loop Prevention
The DUAL protocol is equipped with an administration of a mechanism that prevents routing loops during the selection of the network’s pathways. The built-in integration increases the networking capabilities by eliminating transmission delay and the occurrence of packets and also unnecessary transmission of packets.
Classless Routing
It supports classless routing through Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM), enabling efficient use of IP address space. This capability allows networks to be subnetted with precision, optimizing address allocation and improving overall distribution.
Protocol-Independent Operation
It is used as a routing platform for the IPv4 and IPv6 protocol in a single environment, making it easier for the users to work with the two different Layer 3 standards. This flexibility makes it effective to be applied in the current networks that consist of different Layer 3 protocols.
Partial and Bounded Updates
EIGRP makes use of a targeted update mechanism that sends routing information only when changes occur in the network. This approach, known as partial updates, ensures that only the affected routes are communicated, rather than sending the entire routing table. The targeted update functionality is mainly aimed to control the usage of the given bandwidth and maintain the exemplary network performance in the large scale.
Load Balancing
Due to the load distribution of traffic across the equal and unequal path costs, EIGRP supports load balancing. Thus, by having both equal and unequal cost load balancing, it reaches the condition to avoid bottlenecks during the transmission, and therefore, the performance of the network increases and resource utilization improves.
Below, we have explained its metrics along with the composite metric formula.
EIGRP Metrics
EIGRP uses a composite metric to determine the best path to a destination. The metric is calculated based on bandwidth (minimum bandwidth along the path) and delay (cumulative delay of all links in the path) by default.
Bandwidth
The bandwidth metric determines the least value link in a particular path. It loads the best path with higher bandwidth and selects paths that can handle traffic load at a better level to allow efficient data transmission.
Delay
The delay reflects the total time that it takes for information to flow along the particular path in tens of microseconds. Lower the delay values better the paths and are used during the selection of the paths for traffic that requires timely delivery.
Reliability (Optional)
Reliability evaluates the likelihood of successful data transmission over a path. Routes with higher reliability values are preferred, enhancing data delivery success rates, particularly in networks prone to failures or packet loss.
Load (Optional)
Load determines the rainfall usage of a link at any given time. One of the EIGRP features of selecting a path is avoiding paths that are congested to reduce the load or traffic that a network has to handle.
Composite Metric Formula
The composite EIGRP metric is calculated as:
Metric = (K1 × Bandwidth) + (K3 × Delay)
The values of K1 and K3 are adjustable constants set by the network administrator to prioritize specific factors in path selection.
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol makes use of different packet types for communication. Let us discuss in detail.
EIGRP Packet Types
It makes use of five packet types for communication. These are:
Hello Packets
Hello packets are crucial regarding the discovering of a neighbor and maintaining a connection between the routers. They are used frequently to send and acknowledge messages to neighbors making them important components of the structure of EIGRP.
Update Packets
Update packets also contain routing information on other routers that are found in a network. These are only transmitted when there are some changes in the network, hence using limited bandwidth to spread new routing information.
Query Packets
The query packet in EIGRP requests routing information from neighboring routers, allowing a router to gather details about specific routes when it lacks the necessary information in its routing table.
Reply Packets
Reply packets are the answers to the query packets they receive as part of the IP address resolution scheme. They respond to request routing information to other routers which helps in fast overall response to queries and proper routing information maintained in the topology table.
Acknowledgment Packets
They acknowledge updates, queries as well, as reply packets to indicate the reception of the packets. This confirmation provides a positive check and assurance of routing machinery and routing information exchange.
Neighbor Discovery and Adjacency Formation
In Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol, hello packets are used to find out the neighboring routers and also to establish and maintain a relationship. It is an extension whereby routers achieve an agreement on the necessary variables, such as the authentication and key (K) values for exchanging route information. Hello intervals define the amount of time periodically transmitting packets, while the hold timers define the amount of time the device must wait for hello packets.
EIGRP Topology Table
The topology table stores all available routes to a destination. It includes:
- Successor: The best route for a destination, selected based on the lowest metric.
- Feasible Successor: A backup route meeting feasibility conditions, ensuring quick failover when the successor becomes unavailable. Maintaining multiple routes allows it to handle network failures efficiently.
DUAL Algorithm
The Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) ensures EIGRP’s efficiency through loop-free and rapid convergence.
Key Steps:
- Identify Successors: Select primary paths with the best metrics.
- Calculate Feasible Successors: Determine backup routes meeting feasibility conditions.
- Maintain Loop-Free Topology: Ensure stable, efficient routing decisions.
DUAL allows instantaneous routing decisions, enhancing network performance without full recalculations.
Let us now discuss how you can configure it on Cisco routers.
Configuration of EIGRP
Below is a step-by-step guide to configuring EIGRP on Cisco routers:
Step 1: Enable EIGRP
Router(config)# router eigrp 100
Step 2: Configure Networks
Router(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
Step 3: Configure Metrics (Optional)
Router(config-router)# metric weights 0 1 0 1 0 0
Step 4: Enable EIGRP for IPv6 (Optional)
Router(config)# ipv6 router eigrp 100
Router(config-router)# no shutdown
Step 5: Configure Authentication (Optional)
Router(config-router)# authentication mode md5
Router(config-router)# authentication key-chain EIGRP_KEYS
Verification and Troubleshooting
Verify Neighbors
Router# show ip eigrp neighbors
Verify Routes
Router# show ip route eigrp
Troubleshoot EIGRP
Router# debug eigrp packets
This protocol offers several advantages from fast convergence to better scalability. Let us discuss in detail.
Advantages of EIGRP
Some of the advantages are:
- Fast Convergence: DUAL ensures minimal downtime.
- Efficient Bandwidth Usage: Partial and bounded updates reduce network overhead.
- Flexible Metrics: Composite metrics allow better path selection.
- Load Balancing: Supports both equal-cost and unequal-cost load balancing.
- Scalability: Suitable for large networks.
- Protocol Independence: Supports both IPv4 and IPv6.
Limitations of EIGRP
Some of the limitations are:
- Proprietary Nature: Initially restricted to Cisco devices (now an open standard but still heavily Cisco-centric).
- Complex Configuration: Advanced features require careful configuration.
- Resource Intensive: Consumes more CPU and memory compared to simpler protocols.
EIGRP vs Other Routing Protocols
Some of the basic difference between the EIGRP and other routing protocols are:
| Feature | EIGRP | OSPF | RIP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convergence | Fast | Moderate | Slow |
| Scalability | High | High | Low |
| Metrics | Composite | Cost | Hop-Count |
| Protocol Type | Hybrid | Link-state | Distance-vector |
| Vendor Support | Primarily Cisco | Multi-vendor | Multi-vendor |
Use Cases
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol is ideal for:
- Enterprise Networks: Where fast convergence and efficient routing are critical.
- Hybrid Networks: Combining IPv4 and IPv6 routing.
- Large Campus Networks: Where scalability is essential.
Security in EIGRP
It supports several security mechanisms to protect routing information:
- Authentication: It can use MD5 or SHA authentication to ensure that routing updates are received from legitimate sources.
- Filtering: Access Control Lists (ACLs) can be applied to control which routes are advertised or accepted.
- Route Summarization: Limiting the advertisement of specific routes can reduce the risk of route table attacks.
Real-World Scenarios
Some of the real-world scenarios where EIGRP is assisting networks working efficiently are:
Scenario 1: Enterprise Network with Redundant Links
It ensures fast convergence and efficient load balancing across redundant links in a large enterprise with multiple branch offices.
Scenario 2: Mixed IPv4 and IPv6 Environment
EIGRP’s support for both IPv4 and IPv6 makes it an ideal choice for organizations transitioning to IPv6.
Scenario 3: High Availability Data Centers
It ensures minimal downtime and efficient routing in data centers where high availability is critical.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is EIGRP stands for?
The EIGRP stands for enhanced interior gateway routing protocol, which is a unique Cisco innovation used for ease of deployment and fast convergence.
Q2. Why EIGRP is called Hybrid protocol?
It is called hybrid protocol because it uses metrics from both distance vector protocol and link state protocols.
Q3. What are the 3 key features of EIGRP?
Three features of EIGRP are:
- Unequal cost load balancing
- Support for networks 255 hops away
- Rapid convergence features
Q4. Is EIGRP better than OSPF?
If we compare OSPF vs EIGRP, we find that EIGRP has faster convergence time than OSPF. So, yes it is better than OSPF
Conclusion
EIGRP is considered as one of the leading routing protocols that works effectively in Cisco orientated networks. It is widely used in enterprise networks as Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol incorporates the characteristics of both the link-state and the distance-vector protocols while still having the benefits of being fast and flexible in terms of the underlying network. Understanding the characteristics of this protocol and its configuration, as well as the operational behavior, provides information on how to build efficient networks.