Introduction
Understanding the fundamental structures and protocols that govern computer networks is essential for anyone working in the field of networking and cybersecurity. Two well-known models that serve as the backbone of network communication are the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model and the TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) model.
While both models provide a framework for understanding how data is transmitted and received across networks, they differ in their approach and organization. In this blog, we will compare the OSI model with TCP/IP model and understand the difference between OSI and TCP/IP Model. Still, before moving to the differences, we need to understand both these models and their layers.
OSI vs TCP/IP Model
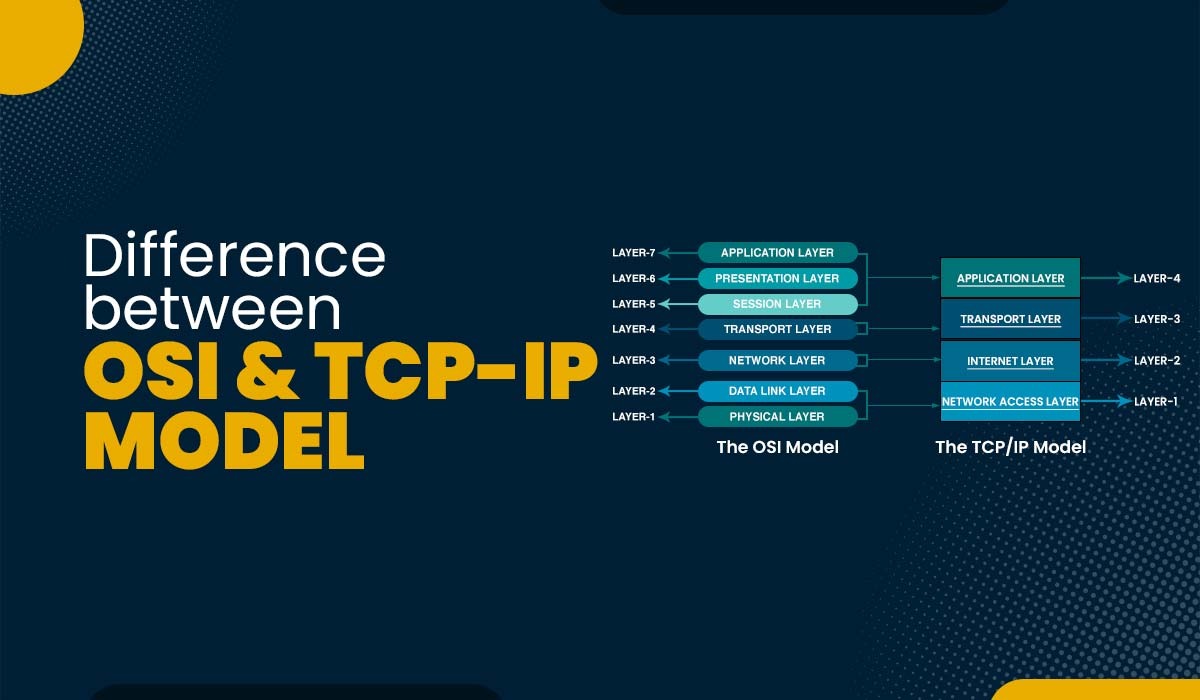
The main difference between OSI and TCP/IP Model is that OSI model has seven layers, while TCP/IP has four and OSI is protocol-independent, whereas TCP/IP is tied to its protocols. Here are some other important differences:
- Structure: OSI has 7 well-defined layers with specific functions, offering a clear roadmap for network communication. TCP/IP has a simpler 4-layer structure, combining functionalities for a more practical approach.
- Purpose: OSI is a conceptual framework, a blueprint for how networking should work on the other hand, TCP/IP is a working protocol suite, the actual set of rules devices use to communicate on the internet.
- Implementation: OSI is not tied to specific protocols, making it adaptable but not directly usable while TCP/IP defines the protocols used on the internet today, making it practical but less flexible for alternative implementations.
Now, let’s move on to understand the OSI model of computer networking in detail.
What is OSI Model?
OSI stands for Open System Interconnection. The OSI Model was developed by (ISO) International Standard organization to help standardize communication between computers.
The original objective behind the OSI model of computer networking was to make communication possible between two different vendors. Because, when the internet was growing at the beginning of the time, different vendors could not communicate with each other and, OSI Model came as the standard model for discussing, teaching, and learning the networking procedures in the field of Information technology.
So, the OSI model was developed, but it was never implemented and remained as just a reference model for study purposes only.
There are 7 layers in OSI Model.
OSI Model Layers
- Layer 1 – Physical Layer: This layer handles data transmission through cables, radio waves, etc.
- Layer 2 – Data Link Layer: This layer makes sure the data transfer between adjacent nodes is error-free.
- Layer 3 – Network Layer: This layer is responsible for routing data packets between different networks.
- Layer 4 – Transport Layer: It makes sure the data is transferred with protocols like TCP and UDP.
- Layer 5 – Session Layer: It manages sessions and connections between network devices.
- Layer 6 – Presentation Layer: This layer handles data formatting, encryption, and compression.
- Layer 7 – Application Layer: This layer supports application services like email and browsing.
These are seven of the OSI Model Layers.
Advantages of OSI Model
- Modular Structure: The model is divided into seven distinct layers, allowing for a clear separation of responsibilities and easier troubleshooting.
- Standardization: The OSI model provides a standardized framework, ensuring compatibility and interoperability between different network components and devices.
- Flexibility: Each layer can be developed independently, allowing for the introduction of new technologies without disrupting the entire network.
- Troubleshooting and Debugging: The layered structure simplifies the identification and resolution of network issues by isolating them into specific layers.
- Interoperability: The model’s standardization fosters seamless communication between network components from different vendors, promoting interoperability.
Disadvantages of OSI Model
- Its practical implementation is restricted as it is purely based on the theoretical model, which does not consider the availability of appropriate technology.
- The TCP/IP protocol was already implemented when the OSI model appeared on the market. So, some companies were resisting initially to use it.
- The initial implementation was very difficult, slow, and expensive because the OSI model is very complex.
- When it was practically deployed, some of the layers like the session layer and presentation layer had a very less functionality.
- Duplication can be found in different layers because different layers provide functions like addressing, flow management, and error correction.
- For practical network implementation, there is a need for sufficient solutions but the standards of the OSI model are theoretical, so it fails to provide adequate solutions.
What is TCP/IP Model?
The TCP/IP Model in Computer Network was designed by the Department of Defense (DOD), and it is based on standard protocols.
The TCP/IP model is also known as IP Stack, and this model is practically being implemented. This model is a widely adopted model due to its simplicity, and it is also known as the concise version of OSI model.
TCP Layers
As compared to OSI Model, there are 4 TCP layers which are:
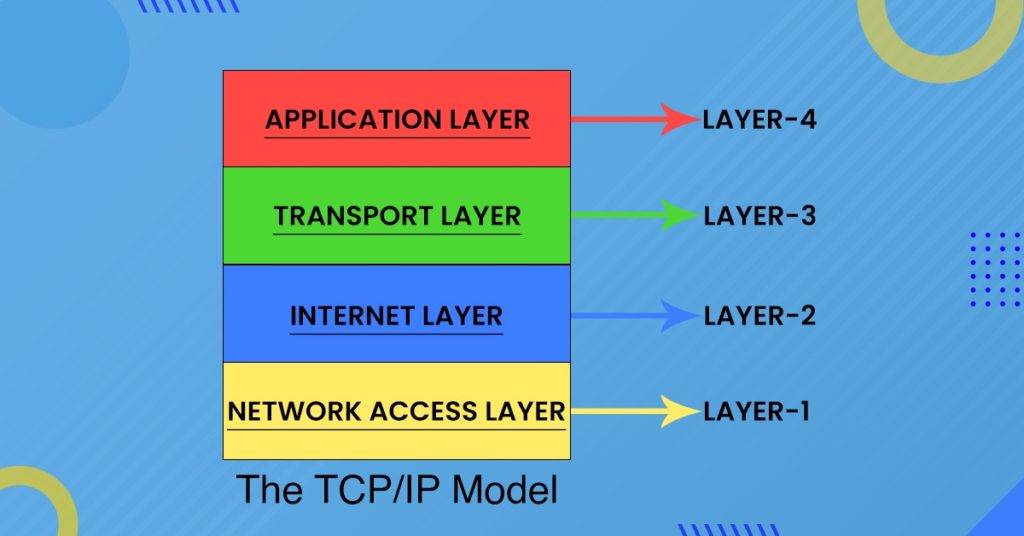
- Layer 1 – Network Interface: This layer combines the Physical and Data Link layers of the OSI Model for hardware communication.
- Layer 2 – Internet Layer: It focuses on addressing and routing via IP.
- Layer 3 – Transport Layer: This layer is responsible for reliable data delivery, and it does that with the help of protocols like TCP.
- Layer 4 – Application Layer: This layer is a combination of the top three layers of OSI Model and handles user interaction.
So, there are 7 layers in the OSI Model whereas in TCP/IP, we only have 4 layers.
Advantages of TCP/IP Model
- OSI Model is also referred to industry-standard model that is applied to real-world networking issues.
- Among heterogeneous networks, it allows cross-platform communications hence called interoperable.
- It can be used by any individual or any organization, as it is not owned by any particular institute, so it is called as an open protocol suite.
- Without any disruption in the current services, networks can be added hence known as a scalable, client-server architecture.
- Each device is made identifiable over the network as OSI Model assigns an IP address to each computer on the network. A domain name is assigned to all the sites which helps the networking professionals to get the name and address resolution services.
Disadvantages of TCP/IP Model
- It can only represent the TCP/IP suite and fails to represent any protocol stack. So, we can say it is not generic in nature.
- The concepts of services, interfaces, and protocols cannot be clearly separate. So, new technologies can never be described in new networks.
- It cannot differentiate the data link and the physical layers, which comprise very different functionalities. A proper effective model must be able to find the difference between the two.
- It is designed and implemented for wide-area networks. Small networks like LANs and PANs, which are personal area networks, cannot be optimized for it.
Despite having many differences between the two, there are some similarities.
Similarities between OSI and TCP/IP Model
- Both TCP/IP and OSI are logical models.
- They are arranged layer wise, therefore referred as an architectural model. All the protocols are arranged in every layer and both of them have the same set of protocols.
- Both of them define the standard for networking.
- For creating and implementing networking standards and devices, both of them provide frameworks.
- Both of them help in simplifying and dividing network communication into making their layers.
- Both models allow manufacturers to design sets of devices and networking components that can coexist and work with those made by other businesses.
- In both models, a single layer establishes a set of standards and defines a certain functionality.
- By dividing the layer’s complex functions into simpler components of the layer, both models simplify their troubleshooting process
Now, let’s see the comparison of OSI Model vs TCP/IP Model.
Difference between OSI and TCP/IP Model
Here are the key differences between TCP/IP and OSI Models in a tabular form –
| Parameters | OSI Model | TCP/IP Model |
| Full Form | Open Systems Interconnection | Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol |
| Layers | OSI Model has 7 Layers | TCP/IP Model has only 4 Layers |
| Development | It was developed by ISO | It was developed by DOD |
| Usage | Its the reference model used for study purposes, never implemented | This is the concise version of OSI, and it is logical model which is being implemented |
| Approach | It follows a vertical approach | It follows a horizontal approach |
| Service | Provides quality services | Doesn’t provide quality services |
| Dependency | It is a protocol-independent standard, and it acts as a communication gateway between network and end-user. | It is based on standard protocols. This is a protocol for communication that allows hosts to connect to networks. |
| Delivery | It guarantees the delivery of package | It doesn’t guarantee package delivery |
| Reliability | Less Reliable | Very Reliable |
| Ease of Change | Changes can be done easily in this model | It is not easy to make changes in TCP/IP Model. |
These are the main difference between OSI and TCP/IP model. You can best learn about OSI and TCP/IP networking model in Cisco CCNA training by PyNet Labs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the difference between TCP IP model and OSI model?
The TCP/IP model consists of four layers and is widely used for Internet communication, while the OSI model consists of seven layers and is primarily a reference model. The TCP/IP model is more flexible and widely adopted, whereas the OSI model offers a more comprehensive approach to networking but has limited implementation.
Q2. What are the similarities between TCP and OSI models?
Both the TCP/IP model and the OSI model have a layered structure, describe the flow of communication, and support protocol independence. They both use data encapsulation and handle segmentation and reassembly. However, the TCP/IP model is more widely used, particularly in relation to the Internet.
Q3. What is the difference between TCP IP protocol and TCP IP model?
The TCP/IP protocol refers to the specific suite of communication protocols used for network communication. The TCP/IP model, on the other hand, is a conceptual framework that categorizes and organizes these protocols into four layers to understand their functionality and interaction within the network.
Q4. Do we use OSI model or TCP IP model?
In practice, the TCP/IP model is predominantly used in networking, especially for the Internet and modern networks. The TCP/IP model’s widespread adoption is due to its close association with the development and functioning of the Internet. While the OSI model provides a conceptual reference framework, it is not as commonly implemented as the TCP/IP model.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have discussed the difference between OSI and TCP/IP Model and also pointed out the similarities between the two. In conclusion, both the TCP/IP and OSI models serve as essential frameworks for understanding and implementing network protocols. The TCP/IP model, with its practicality and flexibility, has become the standard model for the Internet and modern networks. Its advantage lies in its wide adoption, efficiency, and alignment with real-world networking practices.
On the other hand, while the OSI model offers a comprehensive and modular approach to networking, its disadvantage is its limited implementation. Despite this, both models have played a crucial role in shaping the networking industry and have provided valuable insights into the layered nature of network communication. Understanding these models is essential for networking professionals, enabling them to navigate the complexities of modern networking and ensure seamless communication across the globe.
We hope you liked this comparison of OSI Model vs TCP/IP Model, do share your valuable feedback in the comment box below.