Introduction
EIGRP vs OSPF – it’s a debate as old as networking itself. Whether you’re a seasoned network engineer or just starting out, understanding the differences between these two protocols is crucial to building a reliable and efficient network.
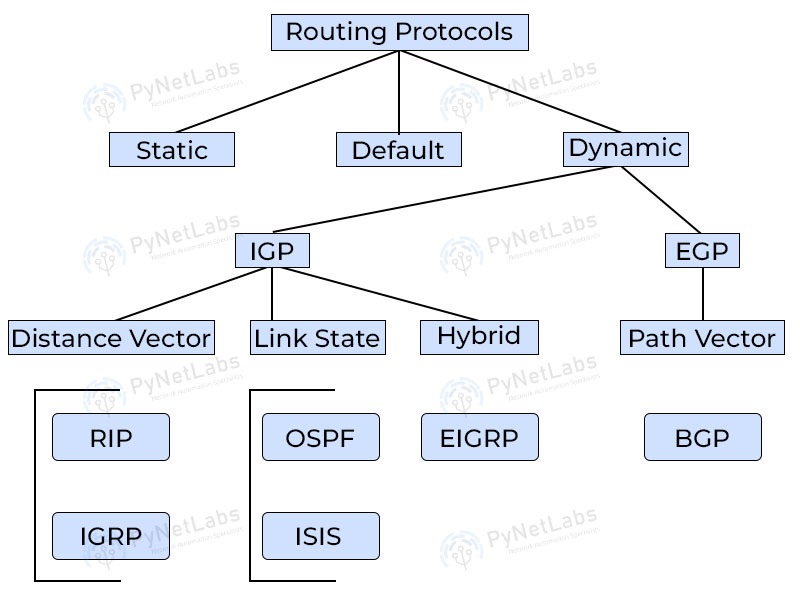
The automatic and dynamic exchange of routing information between routers is made possible by routing protocols. As different networks are implemented in different ways, many routing protocols are available, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) are two of the most widely deployed routing protocols currently. EIGRP vs OSPF will give a better understanding of both routing protocols.
In this blog, we are going to talk about the difference between EIGRP and OSPF. We will be comparing both protocols based on the category they both fall into, how they are different on the basis of their metrics, their Administrative Distance, their timers, and load balancing. So let’s get started and understand the differences between these two AMAZING routing protocols.
You should also check out our OSPF BGP Course, which is currently available at great discount.
EIGRP vs OSPF
When we compare EIGRP vs OSPF, we find out that, in OSPF, different routers understand different parts of topology, which they share using LSAs (Link State Advertisements). Using these LSAs, they collect information on the whole topology. In contrast, EIGRP uses the Reliable Transport Protocol (RTP) to send, control, and acknowledge EIGRP updates under DUAL to find the best loop-free route.
| Sr. No. | Comparison | EIGRP | OSPF |
| 1. | Stands for | Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol | Open Shortest Path First |
| 2. | Protocol type | Hybrid | Link State |
| 3. | Administrative distance | 90 (Internal) 170 (External) | 110 |
| 4. | Algorithm | DUAL distance vector | Dijkstra link state |
| 5. | Standards-based on | Cisco Proprietary | IETF Open Standard |
| 6. | Routing metrics | Combination of bandwidth, reliability, load and delay | Interface bandwidth |
| 7. | CPU requirements | Lower CPU and memory needs | Require high CPU and memory |
| 8. | Ease of implementation | Easy but no provision of auto-summary | Complicated |
| 9. | Organized as | It lacks a hierarchical structure | It is hierarchically organized |
| 10. | Used by | It is primarily utilized by medium-sized to large-sized networks | It primarily serves larger organizations in networks |
| 11. | Denoted by | The symbol “D” is used to denote EIGRP in routing table | The symbol “O” is used to denote OSPF in routing table |
| 12. | Algorithm used | The DUAL (Diffusing Update Algorithm) algorithm is used by EIGRP | The DIJKSTRA algorithm is used by OSPF |
| 13. | Administrative boundary | Autonomous System (AS) no. is used to create a separate administrative boundary in a network | Area no. is used to create a separate administrative boundary in a network. The route information is exchanged by the routers from the neighbour routers in the network that exists within the same area |
These are difference between EIGRP and OSPF. Before moving further and discussing these differences in detail, let’s take a look at both these protocols individually.
What is EIGRP?
EIGRP stands for Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol. It is a Cisco proprietary routing protocol used in computer networks to exchange routing information among routers. EIGRP is categorised as an advanced link-state and distance vector routing protocol since it combines their finest qualities.
It is more effective and efficient than previous network protocols, such as Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP) or Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
How EIGRP Works?
EIGRP operates by using a distance vector approach with enhancements from link-state concepts. It employs the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to calculate the shortest path and ensure loop-free routing.
Features of EIGRP
Some features of EIGRP are:
- It is capable of finding alternate paths in case of link failure.
- It ensures loop-free paths using DUAL Algorithm.
- Combines benefits of both distance-vector and link-state protocols.
- It reduces routing table size by summarizing routes.
- It can work with both IP versions: IPv4 and IPv6.
Advantages of EIGRP
- Fast Convergence
- Advanced Metric Calculation
- Load Balancing
- VLSM and CIDR Support
- Scalability
- Neighbor Discovery
- Compatibility
Disadvantages of EIGRP
- Cisco Proprietary
- Setup can be complicated
- Less effective in very large or multi-vendor networks
- Higher CPU and memory usage
- Advanced features make troubleshooting harder
- It can cause routing issues if misconfigured
- Lacks IETF standardization
- Incorrect metrics lead to inefficient routing
What is OSPF?
OSPF stands for Open Shortest Path First. It is a link-state routing protocol used in computer networks to determine the best path for routing IP packets. OSPF is an interior gateway protocol (IGP) designed for use within an autonomous system (AS), which is a collection of networks under a single administrative domain.
OSPF is widely used in large-scale networks, such as enterprise networks and the internet, due to its scalability, fast convergence, and support for complex network topologies.
How OSPF Works?
OSPF relies on the Dijkstra algorithm to calculate the shortest path tree for each route. OSPF routers maintain a comprehensive map of the network, sharing link-state advertisements (LSAs) to update routing tables dynamically.
Features of OSPF
- Link-State Protocol
- Shortest Path First Algorithm
- Hierarchical Design
- Dynamic Updates
- Support for Variable-Length Subnet Masks (VLSM)
- Authentication
- Load Balancing
Advantages of OSPF
- Works across different vendors, enabling multi-vendor compatibility
- Quickly adapts to network changes, ensuring minimal downtime
- Effective in large and complex network topologies
- Uses areas to reduce routing table size and processing, which improves performance
- Provides security options to authenticate routing updates
- Sends updates only to specific multicast addresses, reducing network traffic
Disadvantages of OSPF
- Requires in-depth knowledge for setup and maintenance
- Demands more resources, especially in large networks
- Managing multiple OSPF areas can be challenging
- Complex algorithms and hierarchical design can make it harder to troubleshoot
- The initial convergence can be slower, particularly in large networks
- Limited to equal-cost load balancing only
Let’s see the difference between EIGRP and OSPF on the basis of various metrics.
Difference between EIGRP and OSPF in-detail
Here are some detailed difference between EIGRP and OSPF.
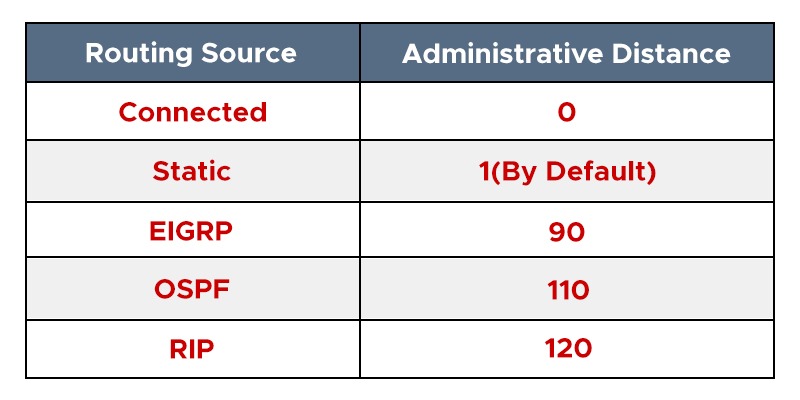
On the basis of Administrative Distance
Administrative Distance is simply the value that defines the trustworthiness of any route. The lesser the AD better the route. For example, if a router learns about the network 192.168.1.0 from 3 different routers, the decision to find the best out of them would depend upon the source of information. Now let’s assume that 1st route was learned via Static Routing, 2nd via RIP, and 3rd via EIGRP.
In this scenario, the 1st route will be installed into the routing table considering the lowest AD associated with the source. In any scenario, the most believable route would be a directly connected route, as it has an AD of 0. Next, preference is given to the static route with the AD of 1.
Now let’s talk about the protocols we are comparing in this blog. EIGRP routes have an AD of 90, whereas OSPF has an AD of 110 which means EIGRP would be given preference in case a route is learned via both protocols. These values are correct when the routes are learned within the same autonomous system. If the routes are getting redistributed from a different autonomous system, the AD of EIGRP routes will be 170, and in the case of OSPF, it remains the same, i.e., 120.
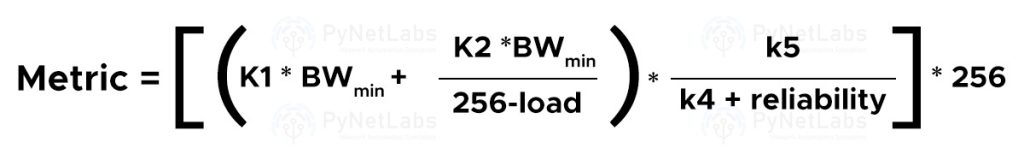
On the basis of Metric they use
OSPF uses the metric of cost, and the path having the lowest cost is elected as the best path to reach the destination. OSPF costs can be calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth (default is 100 Mbps) by the link bandwidth. In EIGRP, the path selection depends on factors like Bandwidth, Delay, Load, MTU, and Reliability. Because load and reliability are dynamic variables, EIGRP’s default metric calculation values are Bandwidth and Delay.
To learn about the metrics of these two protocols in detail, you can click here – EIGRP and OSPF Metric Calculation.
OSPF Cost Calculation –

EIGRP Cost Calculation –
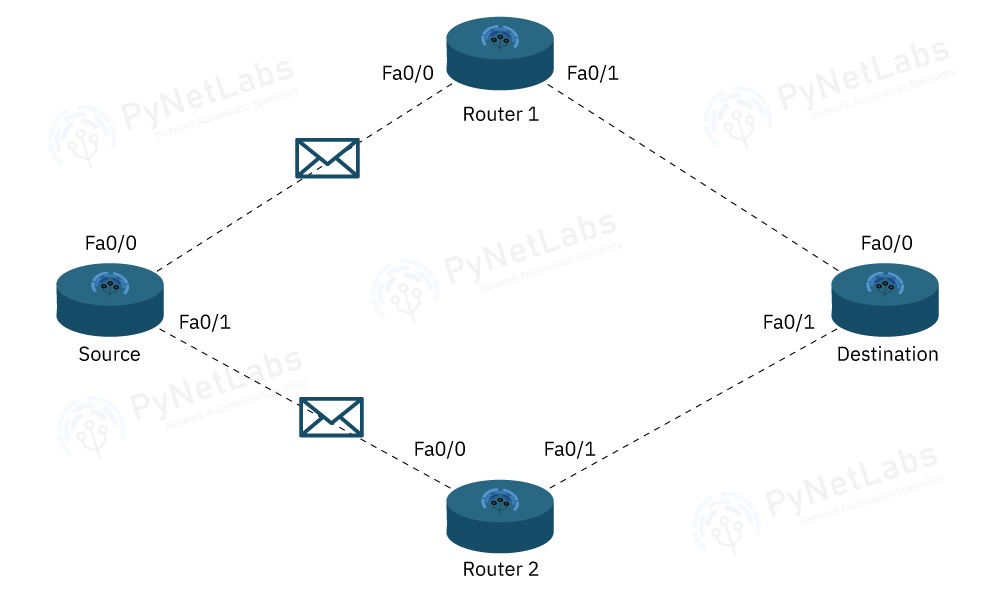
On the basis of Timers
Both the routing protocols, to discover and know about their neighbours, send out hello messages periodically after some interval of time. This interval, known as the hello timer in the case of EIGRP is 5 seconds and 10 seconds in the case of OSPF. And then, there has to be some timer that defines how long a router should wait in case it is not receiving a hello message from the neighbour. This is the case of EIGRP, known as hold-timer, and 3 times of hello time (15 seconds); in the case of OSPF, it is known as dead-interval and is of 4 times of hello time (40 seconds).
Other than the values, another difference between the Hold Time and Dead interval is that Dead Interval defines how long a router will wait for the neighbour to send the hello message. In contrast, hold time is the information we will send to our neighbour telling them to wait for this long in case you stop receiving hello messages from me.
On the basis of Load Balancing
Both protocols by default support equal cost load balancing, meaning if we have more than 1 best route to reach any specific destination, then the data will be distributed on all of the links. In EIGRP, we also see the support for unequal cost load balancing, which can be achieved by manipulating the variance, which is the multiplier of path cost. The good part is that EIGRP intelligently sends proportionally higher traffic on the better links among the available links.
On the basis of Security Features
- EIGRP supports basic security features, including MD5 authentication for securing routing information.
- OSPF offers multiple security options, such as MD5 and SHA authentication, which enhances security in environments where data integrity is critical.
On the basis of Resource Requirements
- EIGRP is relatively light on CPU and memory resources, making it suitable for environments where resources are limited.
- OSPF can be resource-intensive due to its extensive network maps and link-state calculations, demanding more from the CPU and memory.
These are the difference between EIGRP and OSPF. Given you are still with us, you must have a good understanding of both these protocols.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Which is better EIGRP or OSPF?
The superiority of EIGRP or OSPF depends on the specific network environment and requirements. OSPF is an open standard protocol widely supported by various vendors, offering scalability and flexibility. EIGRP, being Cisco proprietary, may provide faster convergence and simpler configuration in Cisco-centric networks.
Q2. What is the main difference between EIGRP and OSPF?
The main difference between EIGRP and OSPF lies in their underlying protocols and vendor support. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol, while OSPF is an open standard supported by multiple vendors. EIGRP is known for its fast convergence and simplicity in Cisco environments, whereas OSPF offers greater scalability, flexibility, and interoperability across different network devices.
Q3. Is EIGRP used anymore?
Yes, EIGRP is still used, particularly in Cisco networking environments. While it is a proprietary protocol, it remains a popular choice for routing within Cisco networks. However, with the rise of open standards like OSPF and the increasing emphasis on multi-vendor interoperability, the adoption of EIGRP has somewhat declined.
Q4. Which is faster among OSPF and EIGRP and why?
EIGRP is generally considered faster than OSPF in terms of convergence speed. This is primarily due to EIGRP’s use of the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL), which allows for faster recalculation and reconvergence of routes.
Conclusion
EIGRP and OSPF are the most widely utilized IGPs today. Both are widely used in corporate networks and are quite mature and robust in their deployment and operation. The goal of this blog is to compare EIGRP vs OSPF to offer you an overview of each protocol and an understanding of the difference between OSPF and EIGRP. In the end, the kind of protocol that works best for your particular network will be determined by several different factors.