Introduction
One of the foundations of modern networking is the border gateway protocol or BGP. Without BGP working in the background to allow system communication, the modern internet as it is known today would not be able to operate. The routing protocol known as BGP has two different versions, i.e., eBGP and iBGP. Both provide the best routing pathways for network communications. In this blog, we will look into the detailed iBGP vs eBGP that better explains these two versions. We will also explain both in detail separately. Let’s Begin!
iBGP and eBGP are part of the BGP protocol which is covered in OSPF BGP Course. Before getting to the difference between the two. Let’s see a brief description of BGP.
What is BGP?
BGP stands for Border Gateway Protocol. It is a exterior gateway protocol that is used to exchange routing information between different Autonomous Systems (AS). Its main responsibility is to select the best route for data travel between the ASes.
- BGP also ensures reliable and efficient data communication over the internet.
- BGP is Path-vector protocol.
- It makes the route decisions based on path attributes.
Difference between iBGP and eBGP
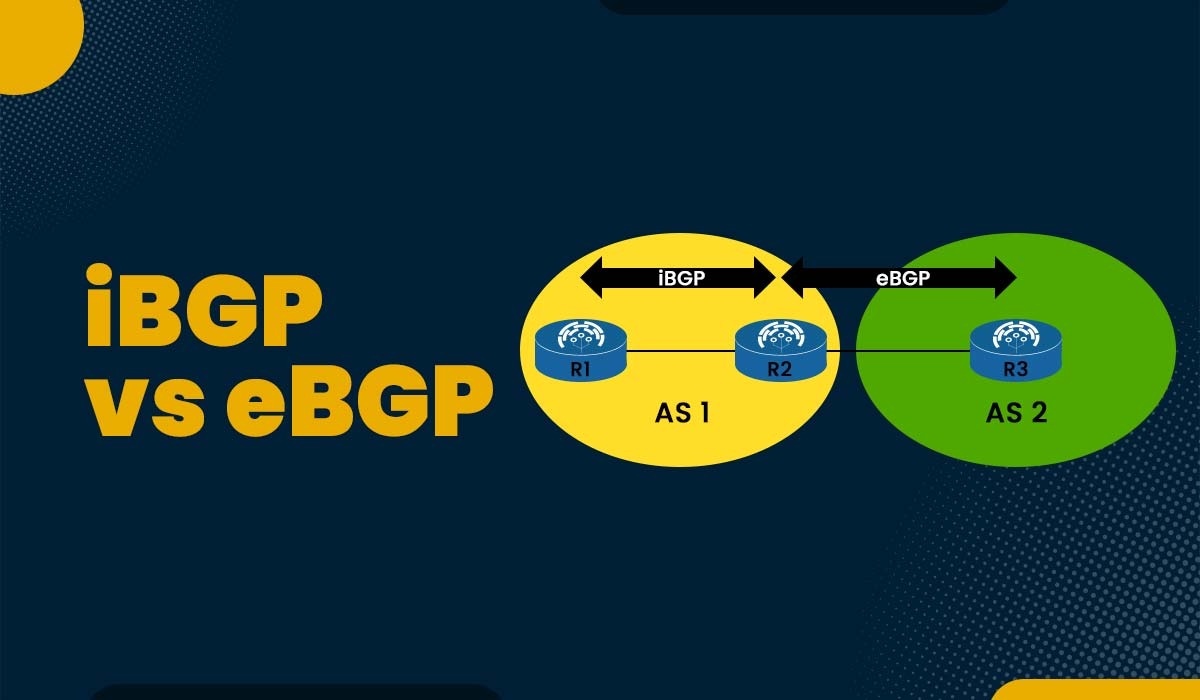
The main difference between iBGP and eBGP is that iBGP shares routes within an autonomous system, while eBGP exchanges routes between different autonomous systems. Below, we have explained more differences between the two in tabular form based on different factors.
| Factors | iBGP (Internal Border Gateway Protocol) | eBGP (External Border Gateway Protocol) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Established between routers in the same AS. | Established between routers in different autonomous systems. |
| Neighborship | Established between routers in the same AS. | Established between routers in different autonomous systems. |
| Route advertisement | Routes received from an iBGP peer cannot be advertised to another iBGP peer but can be advertised to an eBGP peer. | Routes received from an eBGP peer can be advertised to both eBGP and iBGP peers. |
| AS path addition | The local AS number is not added to the AS path attribute when advertising a route to an iBGP peer. | The local AS number is added to the AS path attribute when advertising a route to an eBGP peer. |
| Attributes | Local preference attribute is sent to an iBGP peer. | Local preference attribute is not sent to an eBGP peer. |
| AD | The default administrative distance is 200. | The default administrative distance is 20. |
| TTL | Default peers are set with TTL = 255. | Default peers are set with TTL = 1. |
| Topology | Requires full mesh topology. | Does not require full mesh topology. |
| Loop prevention mechanism | Uses BGP split horizon for loop prevention. | Uses AS path for loop prevention. |
Let’s focus on the eBGP and iBGP in detail to understand the comparison of iBGP vs eBGP.
What is iBGP?
Internal Border Gateway Protocol or iBGP is a BGP version used by routers in the same autonomous system (AS). Without using an IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol), iBGP enables routers to share routing data about external networks, such as the Internet. To avoid routing loops, iBGP peers must create a full mesh topology. iBGP bases its routing choices on network regulations and rulesets by using BGP features like local preference.
Below, we have shown iBGP with two routers, R1 and R2.
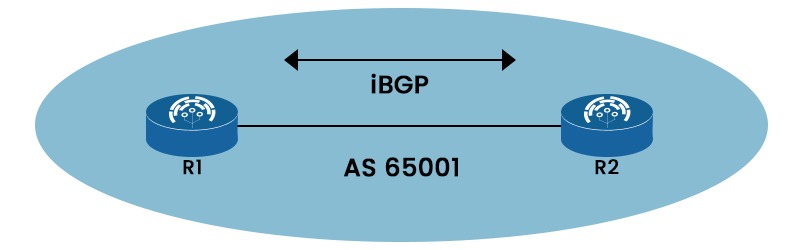
Characteristics of iBGP
- iBGP operates within the same Autonomous System (AS).
- The next-hop addresses remain unchanged when routes are advitised.
- It employs Split-Horizon Rules to prevent loops.
Advantages of iBGP
Below, we have discussed some of the advantages of iBGP.
- Route-Reflection: It is noteworthy that with the help of iBGP, one can facilitate route reflection which ultimately helps to eliminate the need for a large number of iBGP peers as well as makes the network configuration easier.
- Easy Configuration: As far as the BGP routing protocols are concerned, iBGP is relatively easier to be configured than eBGP.
- Improved Network Stability: iBGP helps in enhancing the total network stability and is thus important in any network. It does this by minimizing the effects of routing changes on the system.
- Redundancy: In the case of failures, iBGP offers multiple routes for data transmission to avoid congestion.
Disadvantages of iBGP
Some of the disadvantages of iBGP are:
- Full Mesh Requirement: iBGP requires a Full Mesh of iBGP peers. This results in numerous connections and further raises the network’s complexity level.
- Route Oscillation: Although iBGP is very effective, it is exposed to route oscillation, which in turn makes the network unstable.
- Slow Convergence: It takes relatively more time for the network to attain its stable state in case of a failure or a change.
- Dependence on IGPs: iBGP depends on IGPs in order to function which adds to network complexity and potentially extra failures.
What is eBGP?
An external Border Gateway or eBGP allows communication between several autonomous systems (AS). Network connections via the Internet or between various organizations are made possible by eBGP. eBGP operates in the opposite manner of iBGP, i.e., inside the same AS. eBGP routes don’t need a full mesh topology and have an administrative distance of 20.
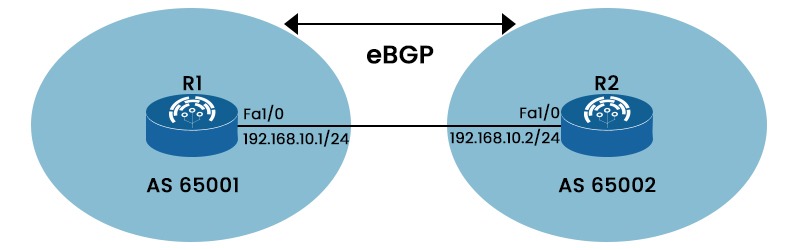
Characteristics of eBGP
- It can operate between different Autonomous Systems.
- Whenever a route is advertised, the next-hop address is updated.
- It employs AS Path Attribute to prevent loops.
Advantages of eBGP
Some of the advantages of eBGP are:
- Inter-AS Connectivity: With the help of eBGP, one can use different AS to connect and further exchange routing information. With this, one can easily communicate between separate networks.
- Flexibility in Route Advertisement: eBGP gives the freedom to network administrators to control which routes are advertised to neighboring AS. This will give them flexibility in routing policies.
- Improved Network Resilience: eBGP assists in improving network resilience by offering multiple paths for data transmission. This will decrease the chances of failures or outages.
- Easy Troubleshooting: With the help of eBGP, it is easier to troubleshoot issues between AS. The reason behind it is each AS can be isolated and can be debugged independently.
Disadvantages of eBGP
Some of the disadvantages of eBGP are:
- Higher Configuration Overhead: Although eBGP is easier than iBGP, it requires more configuration effort. This is because each AS has to be set up individually and peerings have to be formed.
- Route Leaking: eBGP is not safe for use as it often results in route leaking, which in turn causes network instability and security issues.
- Distance Vector Limitations: eBGP uses distance vector routing, which in most cases can result in the formation of routing loops if not well controlled.
- Higher Network Resource Requirements: eBGP is a little more network resource intensive. One of these is bandwidth and processing power, which can, in turn, cause higher costs and jams in the networks.
Now we have a basic understanding of eBGP and iBGP. Let’s understand the difference between iBGP and eBGP in detail.
iBGP vs eBGP
Below, we have compared iBGP vs eBGP in detail based on different factors.
Scope
While IBGP is used for routing information sharing between routers within the same autonomous system, EBGP is used for routing information exchange between routers in different autonomous systems.
As you can see in the picture above, router A in AS 100 and router B in AS 200 are eBGP peers, while router C and router D in AS 100 are iBGP peers.
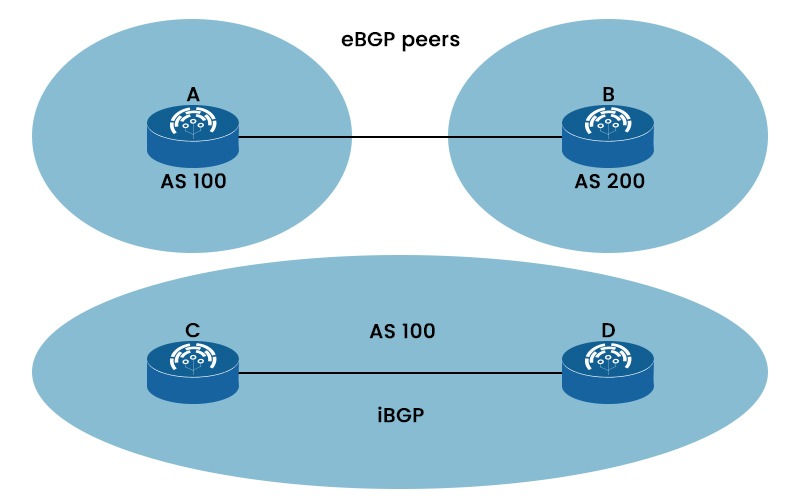
Neighborship
While iBGP peers might be indirectly linked and have the same AS number, eBGP peers are often directly connected and have separate AS numbers. We have shown this in the picture above.
Route Advertisement
iBGP routes obtained from an iBGP peer cannot be advertised to another iBGP peer but may be advertised to an eBGP peer. Conversely, eBGP routes obtained from an eBGP peer can be advertised to both eBGP and iBGP peers.
AS Path Addition
When advertising routes to an eBGP peer, eBGP adds the local AS number to the AS path, but iBGP does not modify the AS path when advertising routes to an iBGP peer.
Attributes
In contrast to iBGP, which sends attributes like local preference to iBGP peers, eBGP does not send such information.
Administrative Distance
The default administrative distance for eBGP is 20, while the default administrative distance for iBGP is 200. This indicates that eBGP routes are automatically favored over iBGP routes.
For example, if router A gets two routes from routers B (having AD 100) and C (having AD 200) for the same destination, it will choose the route from router B since it has a lower AD.
Time-to-live
The default TTL for eBGP peers is 1, while the default TTL for iBGP peers is 255. This implies that iBGP peers might be many hops away; eBGP peers must be directly linked.
Topography
iBGP needs either a complete mesh topology or one of the route reflectors, while eBGP does not. This is so because iBGP forbids peer-to-peer route redistribution.
For example, if an AS has four routers (C, D, E, and F), they must form a complete mesh topology or use other techniques to ensure they all share the same routes.
Loop Prevention Mechanism
iBGP employs BGP split horizon for loop avoidance, while eBGP uses AS path. This implies that although iBGP accepts routes with the same originator ID or cluster list, eBGP does not allow routes with its own AS number in the AS path.
These are the main difference between iBGP and eBGP.
Challenges and their solution with iBGP and eBGP
Challenge with iBGP: One of the biggest challenges with iBGP is need of full mesh. In an AS, every router must establish a direct BGP session with other routers which becomes unmanageable as network grows.
Solution: There are two solutions to this problem:
- Route Reflector: We can use a router as a router reflector which will allow to share the iBGP routes without the need of full mesh.
- Confederations: You can divide the big AS into smaller ASes which will reduce the number of iBGP sessions.
Challenge with eBGP: The biggest concern with eBGP is scaling connections between large Autonomous Systems or multiple ISPs.
Solution: There are two solutions to this problem:
- BGP Communities: Routes are tagged via BGP communities, which makes it easier for network operators to apply particular policies based on tags and streamline complex eBGP configurations.
- Multi-homing: You can use multiple eBGP connections to different ISPs for redundancy and better load balancing.
Use Cases of eBGP
Here are some use cases of eBGP:
- Internet Routing: ISPs use eBGP to exchange routing information with each other.
- Multi-Homed Enterprises: Organizations with multiple ISPs use eBGP for redundancy and load balancing.
- Data Center Interconnects: Large-scale networks use eBGP to connect multiple data centers.
- Cloud Connectivity: eBGP is used to establish connections between on-premises infrastructure and cloud providers.
Use Cases of iBGP
iBGP is useful in scenarios such as:
- Large Enterprise Networks: Used to propagate external routes within an AS.
- MPLS VPNs: iBGP plays a key role in service provider networks.
- Multi-Tiered Network Design: Helps ensure efficient routing in complex networks.
- Route Aggregation: Used in BGP route reflectors to optimize routing.
When to Use eBGP vs iBGP?
Use eBGP when:
- You need to exchange routes between different autonomous systems.
- You are managing internet-facing routers.
- You require inter-AS connectivity for redundancy and load balancing.
Use iBGP when:
- You need to distribute external BGP routes within an AS.
- You are setting up route reflectors to simplify BGP peering.
- You want to ensure consistent routing within your AS.
Now, we have covered everything related to iBGP vs eBGP.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Why is eBGP preferred over iBGP?
eBGP is preferred over iBGP for many reasons, some of these are:
- eBGP AD is 20, and the AD of iBGP is 200. Hence, a BGP router will always choose eBGP over iBGP if the same route is learned from both eBGP and iBGP neighbors.
- It improves scalability because eBGP minimizes the number of iBGP sessions that must be formed inside an autonomous system.
Q2. What is the difference between eBGP and iBGP TTL?
TTL stands for time-to-live. The main difference between the eBGP and iBGP TTL is that eBGP packets have a default TTL value of 1 whereas in the case of iBGP, packets have a TTL value of 255.
Q3. What is the full form of iBGP?
iBGP stands for internal border gateway protocol, and it’s one of the versions of BGP.
Q4. What is the purpose of iBGP?
iBGP is a protocol for exchanging routing information within an autonomous system. It also assists in ensuring consistent and efficient routing among routers within the same network domain.
Conclusion
Both eBGP and iBGP are routing protocols crucial to the functioning of modern computer networks. iBGP vs eBGP gives a clear understanding of which one to choose for better productivity. In this blog, we have covered the detailed differences between the two BGP versions and a brief explanation.