Introduction
A computer network is the main component of the Internet, and it is principally concerned with the transmission of data and communication. It brings us online, lets us exchange content, and lets devices transmit and receive data messages. But what does the term computer network mean?
A computer network is simply a combination of flexible connected devices in a way that they can communicate without difficulty and share some resources as well. Information can be passed through computers, servers, routers, switches, and any other device commonly used in a network. This is the reason why IT professionals or students who wish to secure a career in the vibrant networking industry should have adequate knowledge of the various types of computer networks to handle and manage their preferred architecture.
As we can see in home and organizational networks, different types of networks are used. Hence, it becomes necessary to learn some of the basic features of the network types to enable efficient control of the network. This blog gives insight into what computer networks are all about and how they function and explores different types of computer networks.
Let us first understand what computer networks really are.
What is a Computer Network?
A computer network is a set of interconnected devices that communicate with each other to share resources and exchange data. It can be as simple as two computers connected to share files or as complex as a global network of servers and data centers.
Let’s take an example of a simple computer network:
Imagine you are working in a small office with five employees. Each employee has a computer, and you want to share files and printers between them. You set up a network by connecting each computer to a central switch, which connects to a router. The router provides internet access, and you can now share files, printers, and internet access between all employees.
In this example, the five computers, switch, router, and printer form a small computer network. Each device has a unique address and communicates with each other using standardized protocols.
Now, you must be curious how computer network work. Let us discuss this in detail.
How Does a Computer Network Work?
A computer network exists when computers connect using a combination of hardware and software elements. The hardware can be specific devices such as routers, switches, and Hubs, whereas the software refers to protocols and applications that enable networks.
Network Devices
- Routers: These devices send data packets from one network to the other. They utilize routing tables to establish the best way for data to go.
- Switches: Switches couple one or more devices with a specific network. They control the progression of data flow by channeling it to the right destination.
- Network interface cards (NICs): They are components used in the devices to allow them access to a network.
Network Protocols
- TCP/IP: This is a set of protocols widely implemented on internet connections. It prescribes how information can be presented, located, sent, directed, and taken in.
- HTTP: Hypertext Transfer Protocol is for World Wide Web usage.
- FTP: File Transfer Protocol is applied in file transfer from one device to another.
Data Transmission
- Information is divided into smaller parts; these are called packets.
- Every packet is transmitted and received and then reassembled at the other end.
- Routers and switches organize all devices and use addresses and protocols to ensure that each packet eventually goes to the right place.
Let us now discuss the different types of computer networks in detail.
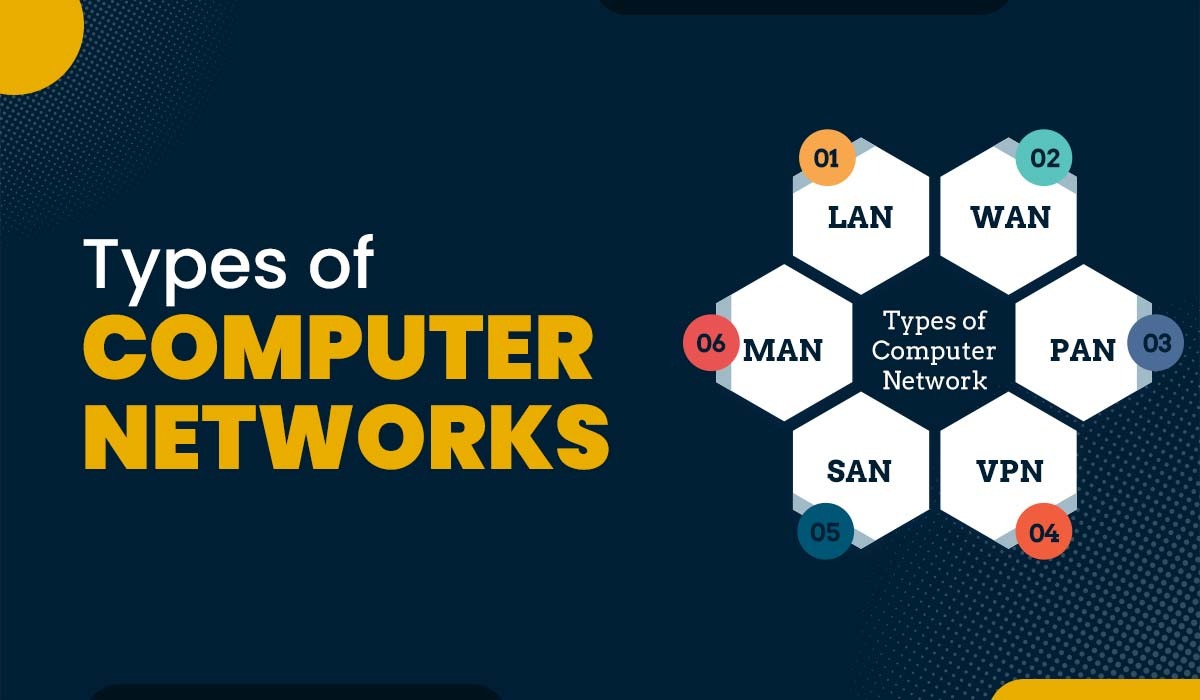
Types of Computer Networks
It is critical for network professionals to understand the various types of computer networks that are known. Each type is unique, exists to fill a particular niche, and is designed to function in specific conditions. Here are eight common types of computer networks:
1. Personal Area Network (PAN)
A PAN is a small network that connects devices at a short range, normally within a few meters of each other. PANs are utilized in devices that relate to individuals, such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
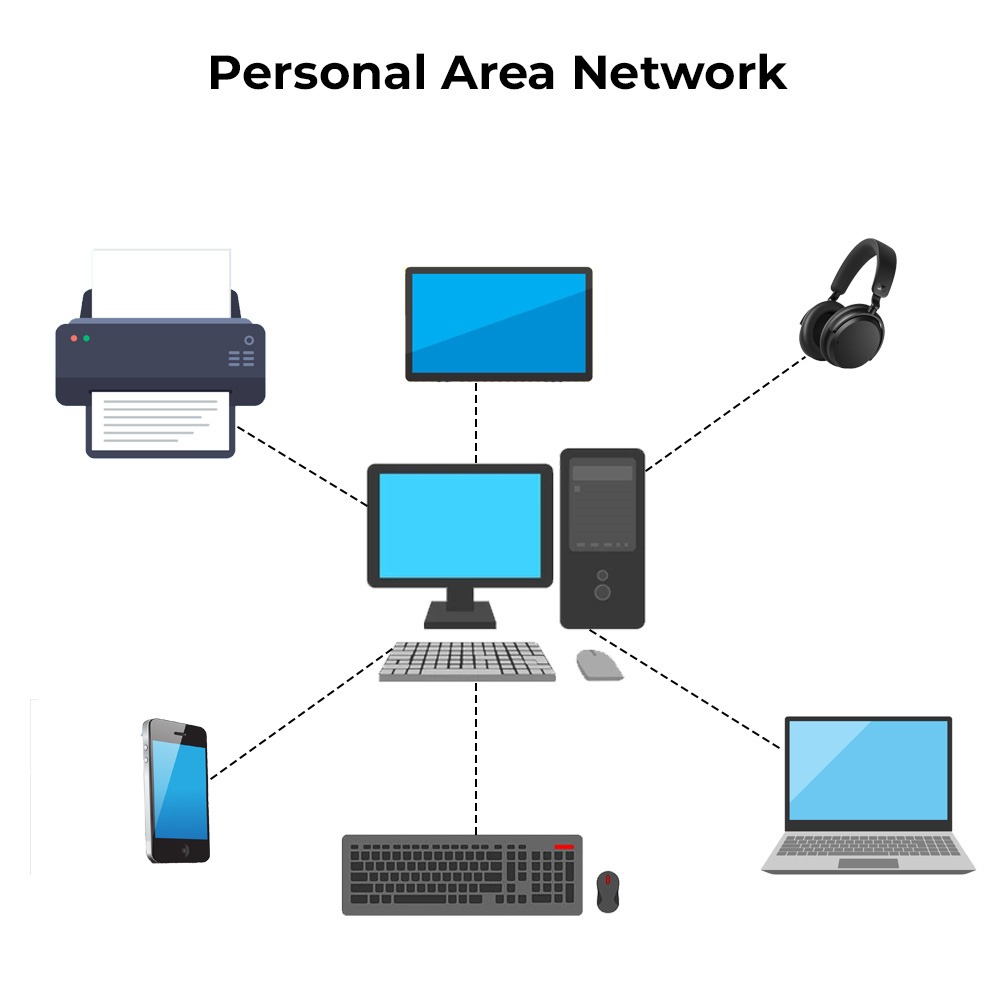
Example: A Bluetooth headset worn by a person who connects it to a smartphone in order to listen to music is a typical example of PAN. Bluetooth is a Personal Area Network wherein the devices establish a connection and can transfer data between them.
2. Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN is a type of network where devices are connected with each other and within a limited geographical area, such as a home, office, or school. Local Area Networks are usually implemented to allow computer sharing or centralization of resources such as printers, files, and the Internet.
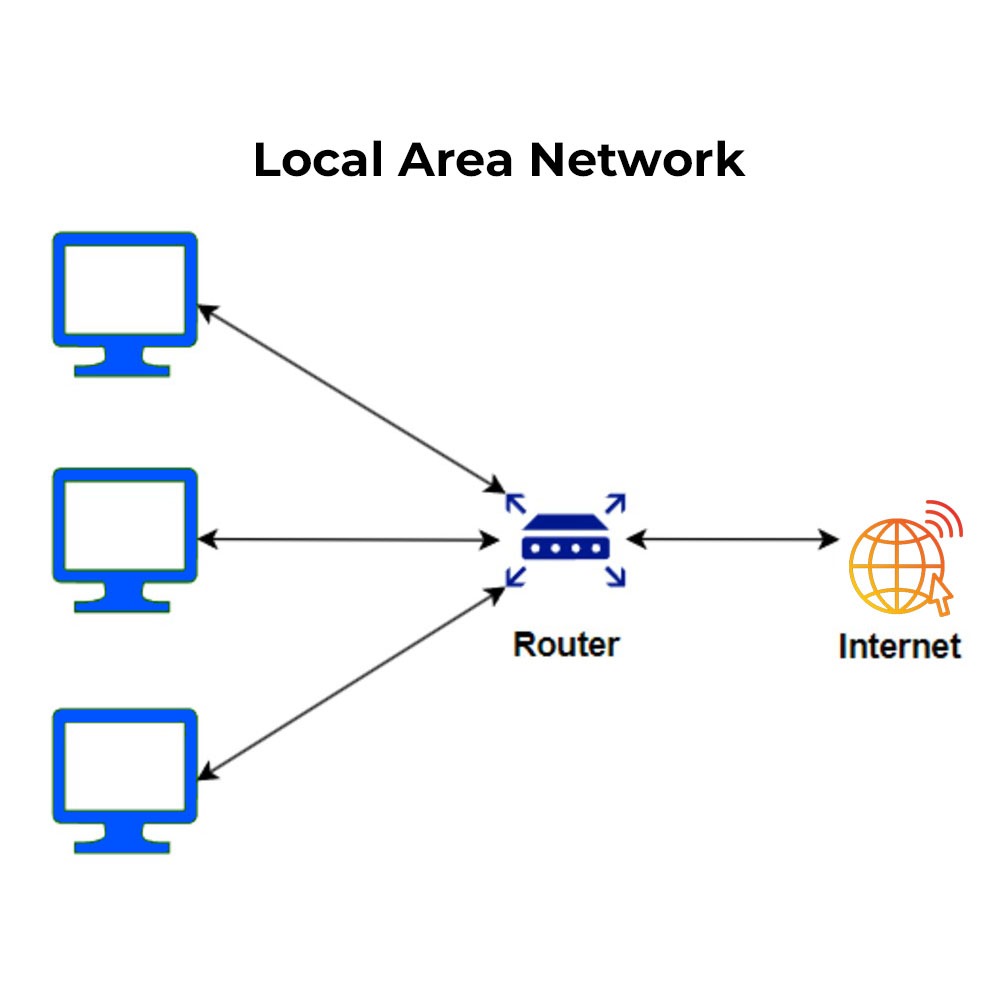
Example: A small office where many connected computers with a central router for files and printing is exemplified by a LAN. The devices are interconnected through preferably Ethernet cables or wirelessly through wireless networks.
3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
MAN is used to connect several LANs together and thus it extends over a larger area, usually a city or a large campus. Today, LANs are combined by many organizations using MANs.
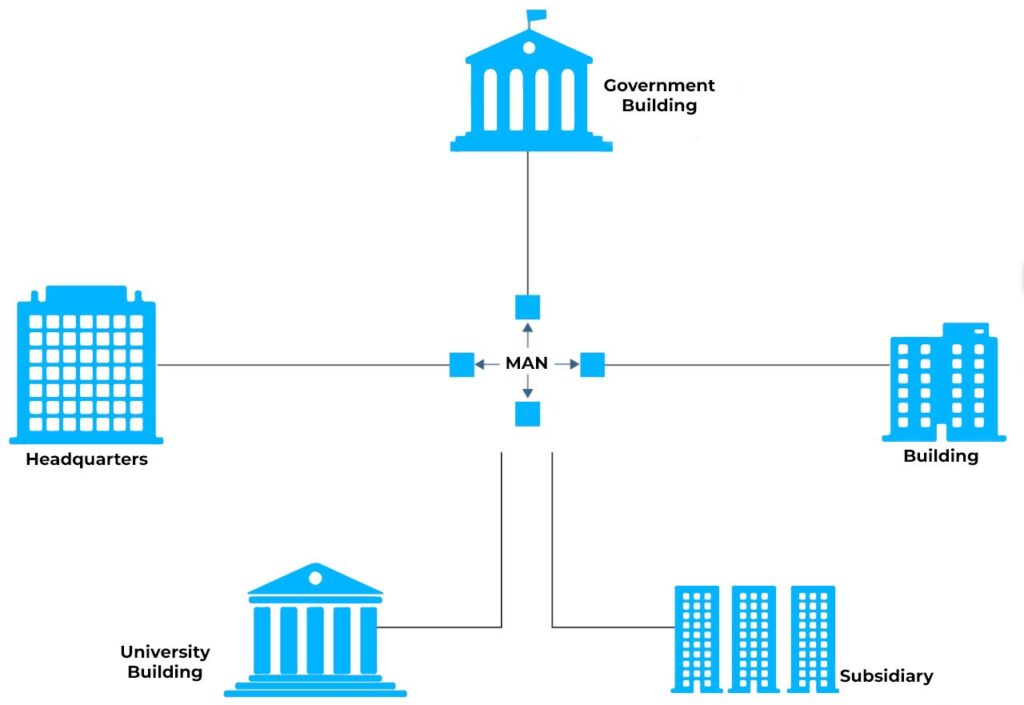
Example: A university, for instance, has many buildings linked with each other using a high-speed fiber-optic cable, known as a MAN. The network enables students and faculty to use resources and communicate in the space across buildings on campus.
4. Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN connects a large geographical area and can extend to several cities, regions, or even countries. WANs are largely employed in large organizations to interconnect a number of LANs or MANs.
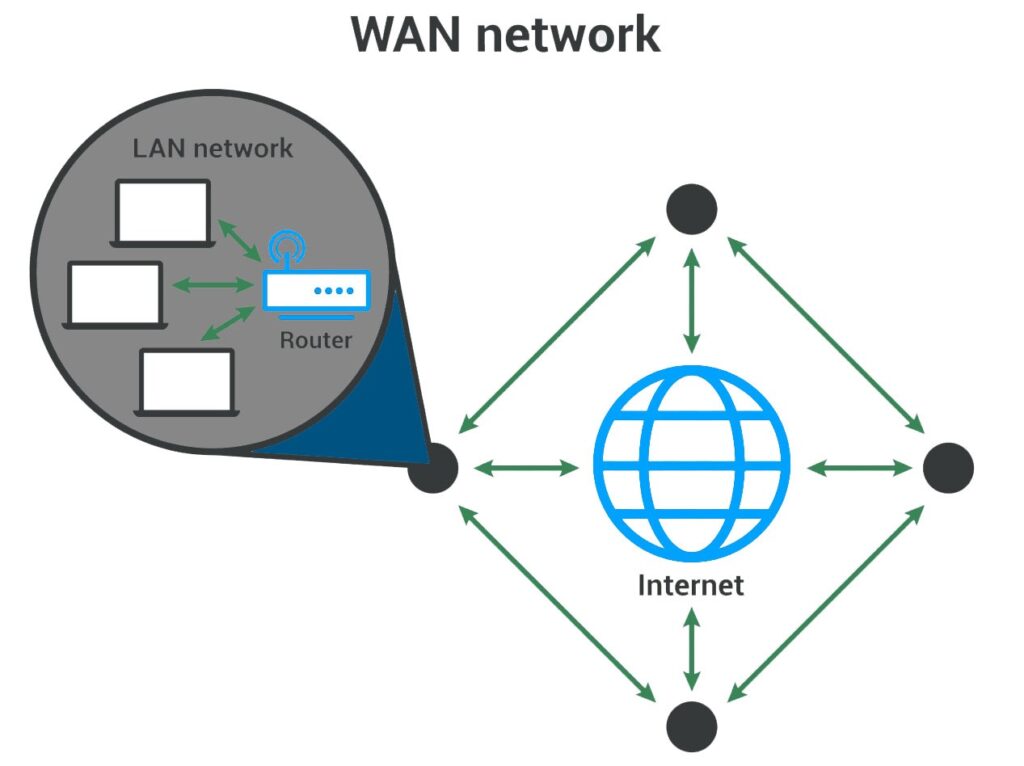
Example: A WAN is a multinational corporation with offices in different countries utilizing dedicated fiber optic links to enable communication. This enables the employees in the different stations to access common assets and share ideas, and information.
5. Storage Area Network (SAN)
SAN is a high-speed network connectivity specifically dedicated to interconnecting switches that allow storage devices to connect to the server. SANs are required where raw data is frequently required through fast and reliable access.
Example: An example of this type of network is a data center in which there are a number of servers that are connected to a storage area network or SAN for its central storage systems. It means that through the help of the SAN, the servers can be capable of acquiring and storing large data in a faster manner.
6. Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
POLAN is a kind of LAN, which mostly implements fiber-optic cables, and passive optical splitters for connection. POLANs are typically faster and more efficient types of networks, which are ideal for conditions in which data must be transmitted at high rates.
Example: The type of network that has multiple connected floors and departments is illustrated by a modern office complex with several floors and departments interconnected through a POLAN. The fiber-optic cables and passive splitters guarantee that the data transmitted is fast and without loss of signal.
7. EPN (Enterprise Private Network)
EPN is the connection between different large organizational offices and is designed to be safe. EPNs are particularly applied to guarantee that the data being exchanged or stored are protected.
Example: An example of this type of network is the network of a financial company with its branches and a central data center linked through an EPN. The EPN guarantees that information such as financials are seamlessly and safely transmitted.
8. Virtual Private Network (VPN)
VPN is a network technology used to create a secure network connection even over an insecure connection like the Internet. VPN can be primarily used when it is necessary to gain access to a private network from a distance.
Example: An example of this type of network is an employee who is working from home via a Virtual Private Network, VPN, to access their employer’s secure network. The VPN makes sure that the particular company resource the employee needs to access is available and can be accessed safely as if the employee is still within the company’s LAN.
These are the 8 types of computer networks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are computer network types?
Computer network types include:
- LAN (Local Area Network)
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- WAN (Wide Area Network)
- PAN (Personal Area network)
- Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
- Virtual Private Network (VPN)
These types of networks are to fill a particular niche and are designed to function in specific conditions.
Q2. What are the 5 classification of computer networks?
The 5 classifications of Computer Networks are:
- LAN (Local Area Network)
- WAN (Wide Area Network)
- PAN (Personal Area Network)
- VPN (Virtual Private Network)
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
Q3. What is Lan Man and WAN?
LAN, MAN, and WAN are types of networks used for different purposes.
- LAN: Covers a small geographical area like an office, school, or home
- MAN: Covers a larger area than LAN, typically a city or large campus
- WAN: Connects devices across extensive geographical areas
Q4. What are three examples of a computer network?
The three most common examples of a computer network are:
- LAN
- MAN
- WAN
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of computer networks is crucial for network professionals and organizations. Each type of network serves a specific purpose and is designed to meet the unique needs of different environments. From a small PAN for gadgets to use in personal life, to a LAN for home or office, a MAN for city or campus, a WAN for a large-scale organization, a SAN to provide fast data transfer, a POLAN for guaranteed data transmission, a EPN for the safe connection, and a VPN for the remote connection – the correct type of network can significantly improve productivity and safety and solely focuses on communication and data transfer.