Introduction
Computer networks consist of interconnected devices that are organized in different ways. The arrangement and communication between these devices are referred to as network topology. The topology chosen impacts the network’s performance, reliability, security, and scalability. There are types of network topologies, including bus, ring, star, mesh, and hybrid configurations. In this blog post, we will be focusing on one topology known as the tree topology. We will look into the definition of tree topology, its purpose, how it operates, and its different types, advantages, and disadvantages.
All these network topologies are very important for network engineers to connect their networks. That is why, these topologies are covered in the very beginning of your networking journey, i.e., CCNA Training.
Before getting into more details, let’s start with understanding this topology.
What is Tree Topology in Computer Networks?
In network topology, there exists a type called tree topology, which is also known as star bus topology. A tree topology, or star-bus topology, is a hybrid network topology in which star networks are interconnected via bus networks. Tree networks are organized hierarchically, allowing each node to have child nodes.
A star network involves connecting all devices to a hub through a cable. The hub itself may be passive or active, depending on the presence of repeaters. On the other hand, a bus network connects all devices to a cable called the bus or backbone.
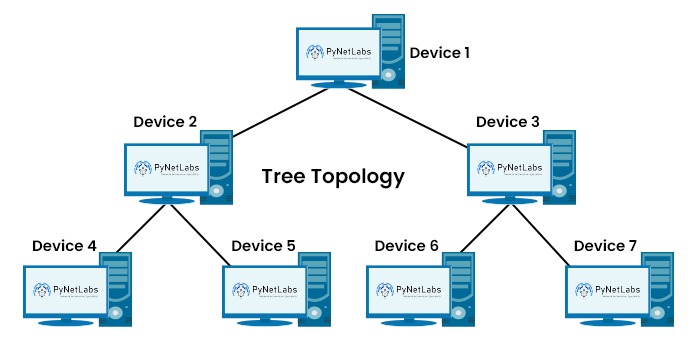
It merges the features of both star and bus topologies. It includes a node known as the root that connects to one or more star networks called branches. Each branch can further extend into sub-branches, forming a structure resembling that of a tree. Below, we have shown the tree topology with the help of a diagram.
Let’s now understand the purpose along with the application of this topology.
Purpose of Tree Topology
The primary purpose of it is to create large and intricate networks that can span over long distances and support multiple devices. Tree network topology also offers hierarchical organizations as well as control over the network.
Here are some practical applications of this topology:
- Internet backbone: The Internet backbone refers to a collection of high-speed networks that connect Internet service providers (ISPs) worldwide. The internet backbone uses this topology to interconnect different ISPs with each other through dedicated channels.
- Military communication Systems: The military employs tree network topology in their communication systems to establish secure and reliable communication between different units and command centers.
- Aircraft navigation systems: Aircraft navigation systems rely on this topology to connect sensors and instruments, on board the aircraft enabling them to transmit data to ground control stations.
Let’s get into the functioning of tree network topology.
How Does Tree Topology Work?
The working of tree topology can be defined over various steps. Below we have explained all the steps and crucial elements.

Root Node or Parent Node
When we talk about the tree network topology, the parent node acts as the root of the tree. This root node can be a hub, switch, or router.
Primary Nodes (Level 1)
These nodes are directly connected to the parent nodes. These are individual networks arranged in the form of star topology. Each primary node either represents a LAN (local area network) or a subnetwork.
Secondary Nodes (Level 2)
Primary nodes can be further branched out into secondary nodes. These are also the star-configured networks. Secondary nodes represent smaller subnetworks within the primary network.
Connection to Backbone

All the central hubs of the primary nodes are connected to a central backbone or bus. This backbone forms the trunk of the tree and allows communication between different primary nodes.
But the question that arises now is how data is transmitted in tree topology.
Data can be transmitted in a tree network topology in two ways. These are:
- Within the individual star-configured networks: Devices that are in the same network segment or star-configured network can communicate with each other via a central hub.
- Between different star-configured networks: When we talk about the communication between different star-configured networks, the data travels through the central backbone to reach the intended destination.
Note: The data that is transmitted in this topology can either be broadcast or point-to-point. The transmitted data can be unidirectional as well as bidirectional.
We now have a basic understanding of what tree topology in computer network is as well as its functioning. Let’s now move on to it’s different types.
Types of Tree Topology
Tree Topology can be classified into 3 categories. These are:
Bus Tree Topology
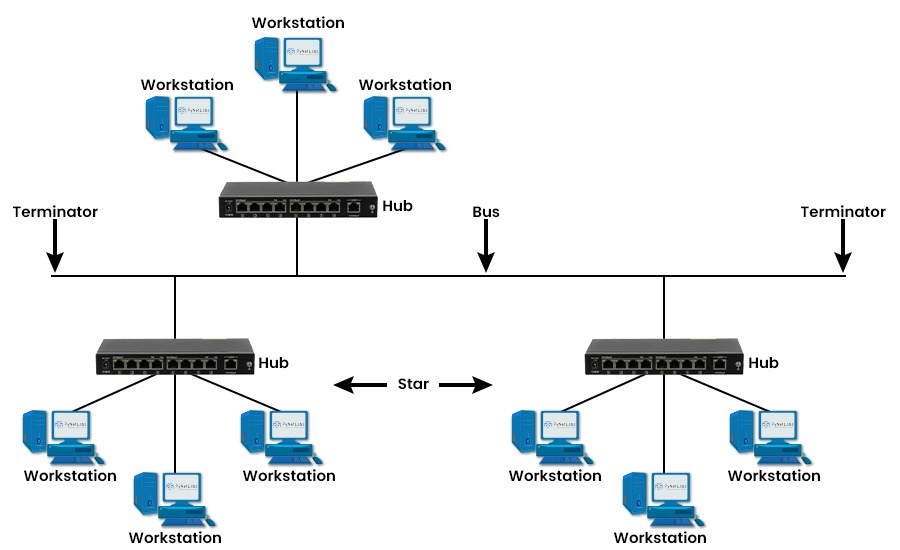
In the bus tree topology, a single cable connects each star network to the bus backbone. This reduces the number of cables needed. It also limits the scalability and reliability of the network. If there is a failure, in the bus backbone it affects the network.
Cluster Tree Topology
In the case of cluster tree topology, multiple cables connect each star network to the bus backbone. This increases redundancy as well as fault tolerance in the network. It also adds to the cost and complexity of cabling. Even if one cable fails, the network can still operate normally.
Spanning Tree Topology
Spanning tree topology is a kind of spanning tree protocol that is organized or configured using the spanning tree protocol. The Spanning Tree Protocol is a network protocol that ensures a loop-free topology for bridged or switched networks.
Features of Tree Topology
Here are some featured of Tree Topology –
- It allows adding more computers to a precise location by expanding the star network connected to the main backbone cable.
- It is fault-tolerant and reliable because the failure of any computer on the network does not affect the operation of the entire computer network.
- With a switch or intelligent hub, it provides a good network performance.
- It is a better choice for small size LAN (Local Area Network).
- It allows for great security, which can also be enhanced through Intelligent Hub.
Application of Tree Topology
Tree topology has several practical applications, the most common of which is its usage in computer networks. It facilitates the connection of networks, enabling communication and data exchange among devices. This topology is particularly beneficial in large-scale networks, such as those found in universities or corporate settings, where it links departments or buildings.
Another way tree structure is applied is in forming star networks where multiple devices are linked to a hub or switch. This configuration is commonly seen in households, workplaces, or small enterprises where devices connect to a router for networking purposes.
How does Data Transmission Work in Tree Topology?
When a device wants to send data to another device in tree topology, it follows a structured path. There is a central device known as the root or main hub. All other devices are connected to it, forming branches. It is possible that these branches may have smaller branches connected to them, which forms a hierarchical structure, as shown in the image.
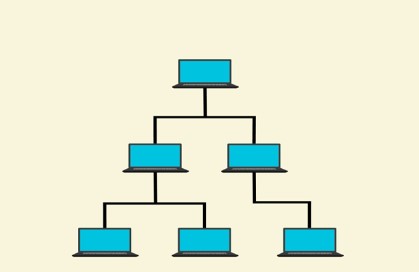
Now, if a device wants to send data to another device, the data transmission follows a specific path. First, the sending device sends the data to the directly connected device, i.e., the parent device. Once the data reaches the parent device, it is further transmitted to the root device. This is the case if the receiving device is on a different branch. Here, the flow of data is upward towards the root device.
If the receiving device is on the same branch, data is easily transmitted via the parent device to the receiving device or via the child device to the receiving device.
Below, we have explained the advantages and disadvantages of tree topology in detail.
Advantages of Tree Topology
This topology offers various advantages as compared to various other topologies. Some of these are:
- Scalability: It is highly scalable as one can expand the devices and subnetworks by adding branches and levels to the network.
- Flexibility: It can accommodate diverse sub-network types and sizes using different hubs and cables.
- Reliability: One can easily isolate errors with in the network without impacting the root node. Hence, it is highly reliable as compared to other topologies.
- Security: Security is everyone’s concern. It enhances security as well as privacy through channels or links.
- It enhances security and privacy through channels or links for data transmission.
- Centralized control: It provides centralized control and management that simplifies network administration tasks such as monitoring, troubleshooting, and security management.
- Efficient Data Transmission: It enables easy data sharing by managing traffic in particular branches. This reduces network congestion and enhances bandwidth usage, especially in networks with heavy traffic.
- Segmentation: Segmentation allows the logical division of the network into smaller, manageable units that represent a different department, location, or function within an organization, providing isolation and security where necessary.
- Point-to-point connection: In tree topology, the root node is connected point-to-point with every other node to provide dedicated bandwidth and reduce data collisions and congestion.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology
Some of the disadvantages of it are:
- Complexity: The installation, configuration, and maintenance of this topology can be complex for multi-level networks.
- Cost: The cost associated with setting this topology up is relatively high as we require cables, hubs, and various other network devices for its proper functioning. Hence, the overall cost increases.
- Dependency: In this topology, if the root node and backbone stop working by any chance, then the overall network will be affected by it.
- Performance degradation: Performance degradation, especially in downstream branches, occurs due to heavy network traffic or if the root node becomes overloaded.
- Single point of failure: The root node behaves like a single point of failure, which means that its failure affects the entire network and makes it inaccessible.
- Parent node affects child nodes: The parent node affects child nodes because the child node is dependent on the parent node, and if the parent device is faulty, then the child node cannot function.
- Maintenance is not easy: In tree topology, the network structure is complex, which makes the maintenance process difficult, and maintenance of the parent device also becomes difficult due to the dependency of the child device on the parent device.
These are the Tree Topology’s Advantages and Disadvantages.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is tree topology and its advantages and disadvantages?
Tree topology is a type of topology that combines the features of both the star and bus topologies. Further at the top is the center or root node, which is further connected to primary or secondary nodes.
It offers advantages such as scalability, flexibility, reliability, security, and better performance. Apart from its advantages, it has disadvantages, like high cost and complexity.
Q2. What is tree topology used cable?
A tree topology combines the characteristics of both the star and bus topology. In this type of topology, star-configured are directly connected to the linear bus backbone cable.
Q3. What protocol is used in tree topology?
One of the protocols used in tree topology is STP, i.e., Spanning Tree Protocol.
Q4. Is tree topology still used?
Yes, tree topology is still utilized in many scenarios. One of many is connecting multiple branch offices to a central office.
Conclusion
A tree topology is a type of computer network where devices are organized in a hierarchical structure. It is a type of hybrid network topology as it combines the features of star and bus topologies. In this blog, we have explained tree topology and its purpose. We have also discussed its functioning and data transmission process. At the end of the blog, we have discussed its types, advantages, and disadvantages.